Plugin installed incorrectly. Rename plugin directory 'swiftmail.backup' to 'swiftmail'.
This translation is older than the original page and might be outdated. See what has changed.
en:software:tim:stencilsTable of Contents
Overview of symbols BPMN 2.0
| Symbol | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
 | Pool | A pool comprises a higher-ranking unit of organisation, e.g. a company. |
 | Swimlane | Swimlanes divide the pool into subordinate units. |
 | Activity | This symbol represents an activity within a process. |
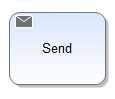 | E-mail / Send | This symbol enables e-mails to be sent automatically and directly from within the process. |
 | Embedded subprocess | This symbol represents an embedded subprocess. |
 | Signal | At this point, the process will be on hold until a certain event or signal occurs. |
 | Start | This symbol marks the starting point of a process. |
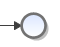 | End | This symbol marks the ending point of this specific branch within the current process. |
 | terminate event | The entire process will be terminated when the termination event occurs. |
 | XOR-Gateway | This symbolizes an exclusive intersection/gateway with one single active output. |
 | AND-Gateway | This symbolizes a parallel gateway at which all available outputs are active. |
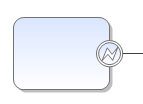 | Boundary Exception | This pathway will be activated in case of an error. |
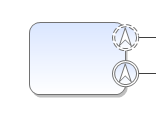 | Boundary escalation | This pathway will be activated in case of an escalation. The current activity will either be terminated (the symbol marked by a non-dashed line) or continued (the symbol marked by a dashed line). |
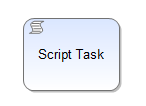 | Script Task | A script task is executed by TIM without any interaction by a user. At the moment, script tasks can only be used in combination with action handlers. The action handler is executed by TIM when the sequence flow arrives. |
 | Manual Task | A manual task is performed only by a user, outside of and without the assistance of TIM or any other application. Therefore, there is no connection to TIM. |
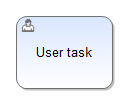 | User Task | A user task is a typical “workflow” task where a user performs the task with the assistance of TIM. In contrast to a manual task, user tasks are performed within TIM. |
 | Automated Task | An automated task uses a service (e.g. a webservice or an automated application). The service is started when the sequence flow arrives at the task. |
Mandatory Handler
Before completing a task, the mandatory handler checks if all mandatory fields of the respective smartform are filled in. If the mandatory fields are empty, the handler prevents the task from completing. Subsequently the user is informed to fill in the mandatory fields.
en/software/tim/stencils.txt · Last modified: 2021/07/01 09:52 (external edit)
