Plugin installed incorrectly. Rename plugin directory 'swiftmail.backup' to 'swiftmail'.
This translation is older than the original page and might be outdated. See what has changed.
en:software:tim:process_structureTable of Contents
The General Structure of a Process
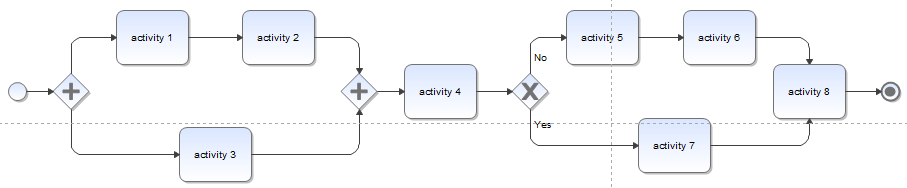
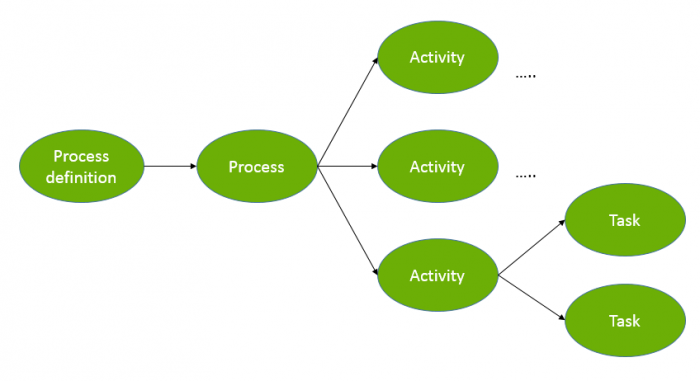
In general, a single process is subdivided into several activities. These activities have to be conducted in a predefined order and finished before the process is considered complete:
Each activity itself covers at least one task that has to be completed. An activity is therefore only finished after all of its tasks are completed. The actual process itself is in turn finished after all its related activities are completed.
en/software/tim/process_structure.txt · Last modified: 2021/07/01 09:52 (external edit)